deep-in-boltdb
to be cont.
bucket -> key/value
Cursor 是内存的概念,记录遍历到 leaf page 的路径
bucket 初始关联了一个 root page,为 db meta page
相关代码,beginTX or beginRWTx 都会有调用
1 | func (tx *Tx) init(db *DB) { |
看下 Cursor 的 search 实现
1 | // search recursively performs a binary search against a given page/node until it finds a given key. |
page 和 node
Once the position is found, the bucket materializes the underlying page and the page’s parent pages into memory as “nodes”
Bucket 的数据结构
1 | // Bucket represents a collection of key/value pairs inside the database. |
bucket 的数据结构
1 | // bucket represents the on-file representation of a bucket. |
继续过 Cursor 的 search 实现: 根据 pageid 获取到 page 或者 node,如果是 page 类型且为 branch or leaf page 则记录到 Cursor 遍历过的 stack 中,否则 panic;node 类型直接记录;判断是否为 leaf (page or node),是的话,在其中 nsearch(key);nsearch 取出 stack 中最后一个 ele,如果 node 不为空,则搜索 node 中的 inode,是否存在该 key
1 | if n != nil { |
page 类型的话,将 ptr 转换为 *[0x7FFFFFF]leafPageElement 数组,即 inodes,在其中二分搜索 key 值
1 | inodes := p.leafPageElements() |
如果 ele 不是 leaf 元素的话,那么只能继续从 node 中查找了 c.searchNode(key, n)
看到这里,记录下 node 的数据结构,越来越接近 B+ tree 的真相了
1 | // node represents an in-memory, deserialized page. |
node 树状关系如图,直觉其中的 pgid 对应的是底层的 page,即 mmap db 文件出来的 byte[] array 中的一块
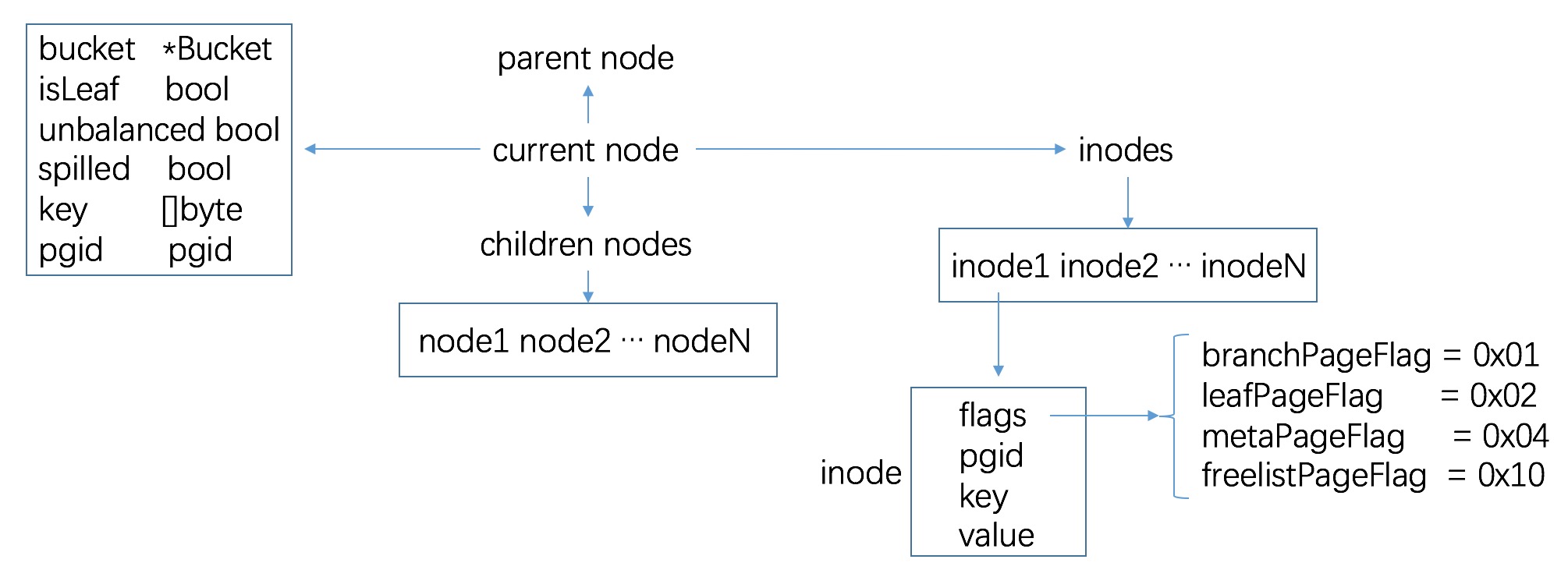
node 的 inodes 数目存储在 page.count 中,下面的代码从 read 中摘出
1 | // read initializes the node from a page. |
branchPage 中只有 key; leafPage 中有 key 和 value
node 中的 key 存储着其第一个 inode 的 key 值;当然如果其没有 inode 则为 nil
1 | // Save first key so we can find the node in the parent when we spill. |
node split,将 inodes 拆分至符合 fillPercent,parent node 的 inodes 也需要添加这些拆分出来的 nodes;还不是特别理解,这么下去的话 root node 岂不是包含所有的 inode,B+ tree 是这么设计的?还不是特别明白