etcd v3.1.9
.wal 文件,即 write ahead log,wal 的实现集中在 wal 目录下
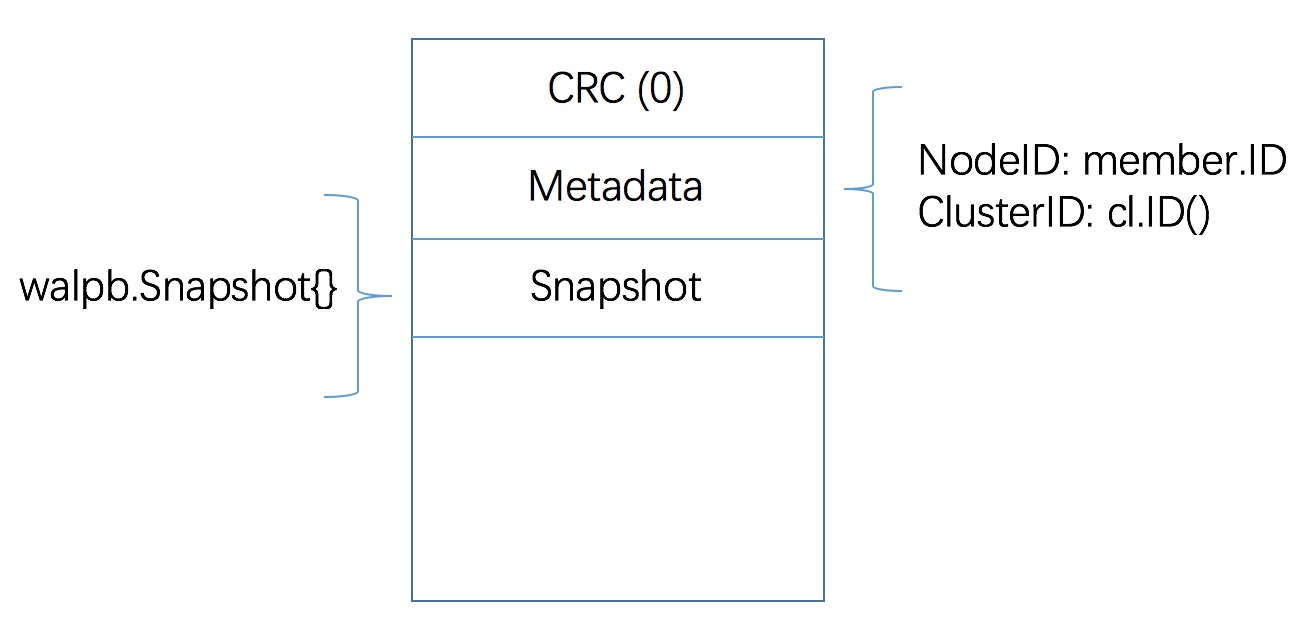
消息类型 其中 wal/walpb 目录下定义了 wal 中记录的两种消息类型: Record 和 Snapshot
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 message Record { optional int64 type = 1 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false]; optional uint32 crc = 2 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false]; optional bytes data = 3; } message Snapshot { optional uint64 index = 1 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false]; optional uint64 term = 2 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false]; }
用 pb 比较省事儿,不用自己实现对象序列化反序列化的逻辑
创建方法 wal 有两个方法会创建 wal 文件,一个是 Create 方法,另一个是 cut 方法
1 p := filepath.Join(tmpdirpath, walName(0, 0))
查看 Create 创建初始 wal 文件的过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 tmpdirpath := filepath.Clean(dirpath) + ".tmp" p := filepath.Join(tmpdirpath, walName(0 , 0 )) f, err := fileutil.LockFile(p, os.O_WRONLY|os.O_CREATE, fileutil.PrivateFileMode) if err != nil { return nil , err } if _, err = f.Seek(0 , os.SEEK_END); err != nil { return nil , err } if err = fileutil.Preallocate(f.File, SegmentSizeBytes, true ); err != nil { return nil , err } ... w.locks = append (w.locks, f) if w, err = w.renameWal(tmpdirpath); err != nil { return nil , err }
w.renameWal(tmpdirpath) 值得抽出来说下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 if err := os.RemoveAll(w.dir); err != nil { return nil , err } if err := os.Rename(tmpdirpath, w.dir); err != nil { return nil , err } w.fp = newFilePipeline(w.dir, SegmentSizeBytes) df, err := fileutil.OpenDir(w.dir) w.dirFile = df return w, err
初始写入 wal 内容示意如下
预分配空间 在 unix OS 上,首先会使用系统调用 Fallocate 预分配文件空间
如果 Fallocate 失败,则 fallback 到 preallocExtendTrunc 再次尝试分配
查看 preallocExtendTrunc 的逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 curOff, err := f.Seek(0 , os.SEEK_CUR) if err != nil { return err } size, err := f.Seek(sizeInBytes, os.SEEK_END) if err != nil { return err } if _, err = f.Seek(curOff, os.SEEK_SET); err != nil { return err } if sizeInBytes > size { return nil } return f.Truncate(sizeInBytes)
在 darwin OS 上,首先会调用 preallocFixed,该函数中使用了系统调用 SYS_FCNTL 预先分配文件空间
如果 preallocFixed 失败,则调用 preallocExtendTrunc 再次尝试分配
编码 / 解码 wal/encoder.go 实现了写入逻辑
File Pipeline wal/file_pipeline.go 用来预创建文件,为后续生成新的 wal 文件使用
fp.Open() 在 cut 方法中被调用,cut 中的调用如下
1 2 3 4 5 newTail, err := w.fp.Open() if err != nil { return err }
而 fp.Open() 从 fp.filec 中获取 locks file 返回
在初始化 file pipeline 方法 newFilePipeline 中启动 fp.run() 协程,查看 fp.run() 实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 func (fp *filePipeline) run () defer close (fp.errc) for { f, err := fp.alloc() if err != nil { fp.errc <- err return } select { case fp.filec <- f: case <-fp.donec: os.Remove(f.Name()) f.Close() return } } }
查看 fp.alloc() 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 func (fp *filePipeline) alloc () (f *fileutil.LockedFile, err error) fpath := filepath.Join(fp.dir, fmt.Sprintf("%d.tmp" , fp.count%2 )) if f, err = fileutil.LockFile(fpath, os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY, fileutil.PrivateFileMode); err != nil { return nil , err } if err = fileutil.Preallocate(f.File, fp.size, true ); err != nil { plog.Errorf("failed to allocate space when creating new wal file (%v)" , err) f.Close() return nil , err } fp.count++ return f, nil }
可见预生成了 [0-1].tmp 文件,并对该文件加了锁,待调用 fp.Open() 方法获取使用
Cut 方法 wal 文件大小上限为 64MB
因此当写入消息之后, wal 文件大小 > 64MB 时,会调用 cut 方法
截断之前的 wal 文件,并生成新的 wal 文件用于写入
cut 的整体思路
截断当前使用的 wal 文件
从 file pipeline 中获取 tmp 文件
向 tmp 文件中写入必要的 headers
将 tmp 文件 rename to wal 文件,新文件名为 walName(w.seq()+1, w.enti+1)
将新 wal 文件加入 locks slice 中,并生成 newFileEncoder 用于写入新 wal 文件
详细阅读 cut 方法(保留了原注释)
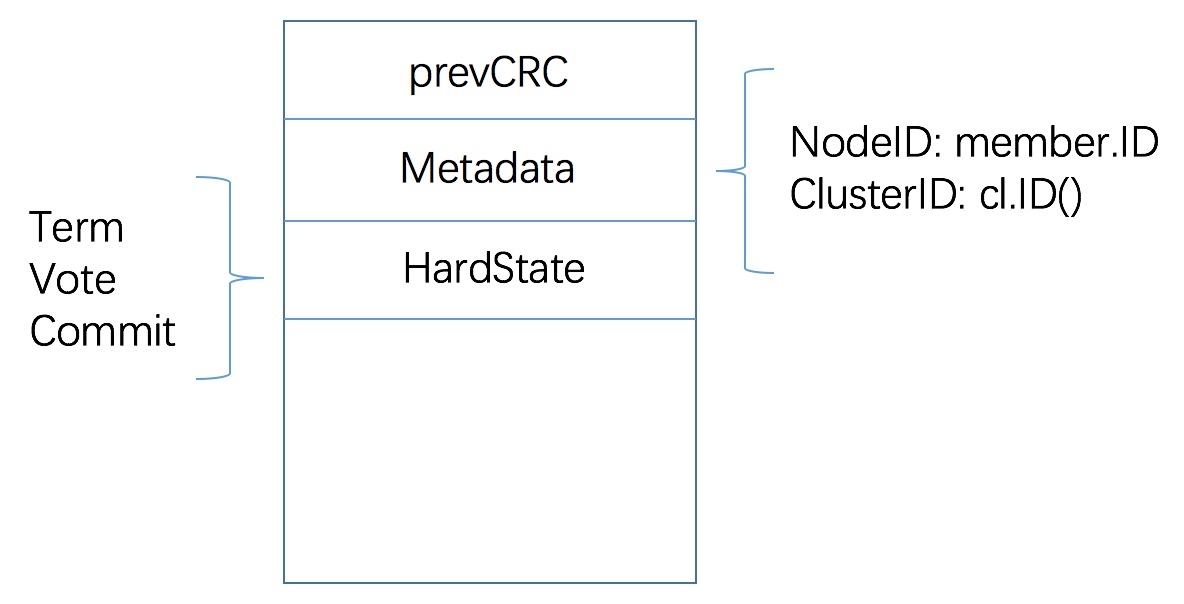
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 func (w *WAL) cut () error off, serr := w.tail().Seek(0 , os.SEEK_CUR) if serr != nil { return serr } if err := w.tail().Truncate(off); err != nil { return err } if err := w.sync(); err != nil { return err } fpath := filepath.Join(w.dir, walName(w.seq()+1 , w.enti+1 )) newTail, err := w.fp.Open() if err != nil { return err } w.locks = append (w.locks, newTail) prevCrc := w.encoder.crc.Sum32() w.encoder, err = newFileEncoder(w.tail().File, prevCrc) if err != nil { return err } if err = w.saveCrc(prevCrc); err != nil { return err } if err = w.encoder.encode(&walpb.Record{Type: metadataType, Data: w.metadata}); err != nil { return err } if err = w.saveState(&w.state); err != nil { return err } if err = w.sync(); err != nil { return err } off, err = w.tail().Seek(0 , os.SEEK_CUR) if err != nil { return err } if err = os.Rename(newTail.Name(), fpath); err != nil { return err } if err = fileutil.Fsync(w.dirFile); err != nil { return err } newTail.Close() if newTail, err = fileutil.LockFile(fpath, os.O_WRONLY, fileutil.PrivateFileMode); err != nil { return err } if _, err = newTail.Seek(off, os.SEEK_SET); err != nil { return err } w.locks[len (w.locks)-1 ] = newTail prevCrc = w.encoder.crc.Sum32() w.encoder, err = newFileEncoder(w.tail().File, prevCrc) if err != nil { return err } plog.Infof("segmented wal file %v is created" , fpath) return nil }
所以 cut 方法初始写入 wal 的内容示意如下
Sync 方法 在 wal 中有如下几个地方使用了 sync 方法
func (w *WAL) Save(st raftpb.HardState, ents []raftpb.Entry) error {}
func (w *WAL) cut() error {}
func (w *WAL) SaveSnapshot(e walpb.Snapshot) error {}
func (w *WAL) Close() error {}
sync 直接来说是使用了系统调用 fsync,确保数据写入磁盘持久化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 func (w *WAL) sync () error if w.encoder != nil { if err := w.encoder.flush(); err != nil { return err } } start := time.Now() err := fileutil.Fdatasync(w.tail().File) duration := time.Since(start) if duration > warnSyncDuration { plog.Warningf("sync duration of %v, expected less than %v" , duration, warnSyncDuration) } syncDurations.Observe(duration.Seconds()) return err }
重点看下 func (w *WAL) Save(st raftpb.HardState, ents []raftpb.Entry) error 方法,毕竟它调用频率较高
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 func (w *WAL) Save (st raftpb.HardState, ents []raftpb.Entry) error ... mustSync := mustSync(st, w.state, len (ents)) ... curOff, err := w.tail().Seek(0 , os.SEEK_CUR) if err != nil { return err } if curOff < SegmentSizeBytes { if mustSync { return w.sync() } return nil } return w.cut() }
从上: vote / term 变化,或有 entries 要写入时,调用 w.sync